
Sludge thermochemical treatment
An introduction to sludge thermochemical treatment methods
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
Pyrolysis is the decomposition of organic matter at elevated temperatures (300 and 1300 °C) in the absence of oxygen at atmospheric pressures. The useful products generated are a charcoal-like biochar solid product, a bio-oil formed from ‘condensable’ volatile substances and ‘non-condensable’ gases which may include both carbon dioxide and methane.

An introduction to sludge thermochemical treatment methods
Thermochemical methods are used for either degrading the sludge solids or pre-treating sludge upstream of anaerobic digestion
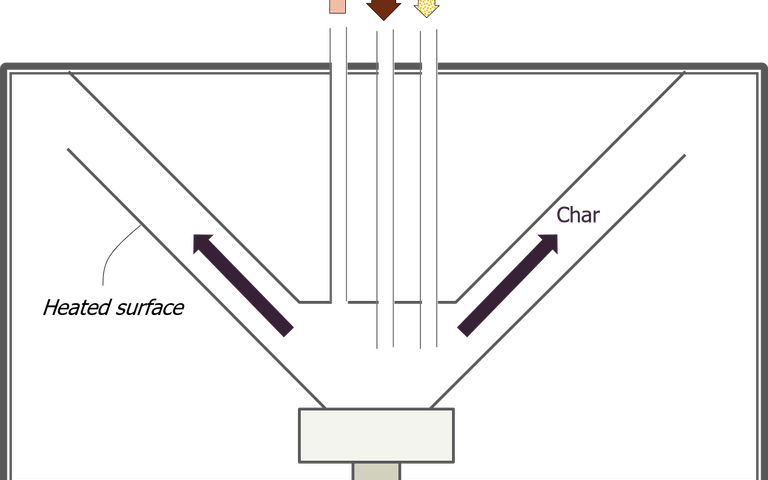
Various reactor configurations exist for sludge thermochemical treatment which vary in design, operation and application
An introduction to non-oxidative sludge thermochemical treatment methods

Pyrolysis refers to the decomposition of organic matter at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen and water
An animation demonstrating 'fast pyrolysis' producing bio-oil as the final product. This video is made available as part of the biofuels education projects funded by the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
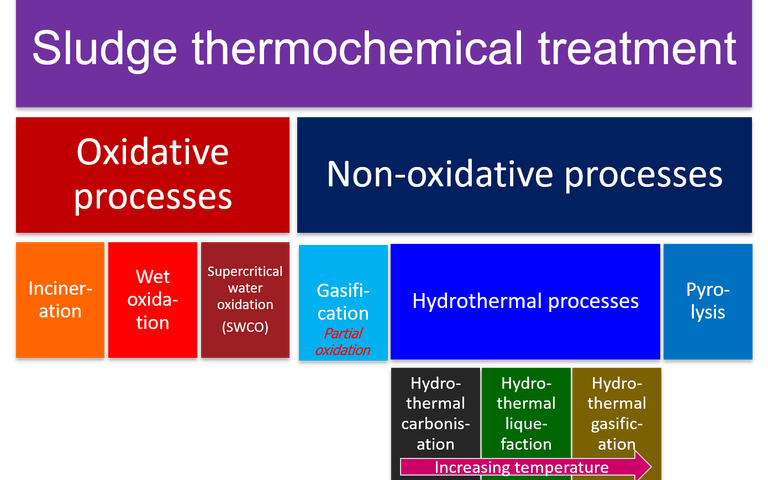
Gasification is conversion at very high temperatures in a partial reducing atmosphere to generate a syngas product
Hydrothermal processes employ elevated temperatures and pressures in wet conditions and in the absence of oxygen
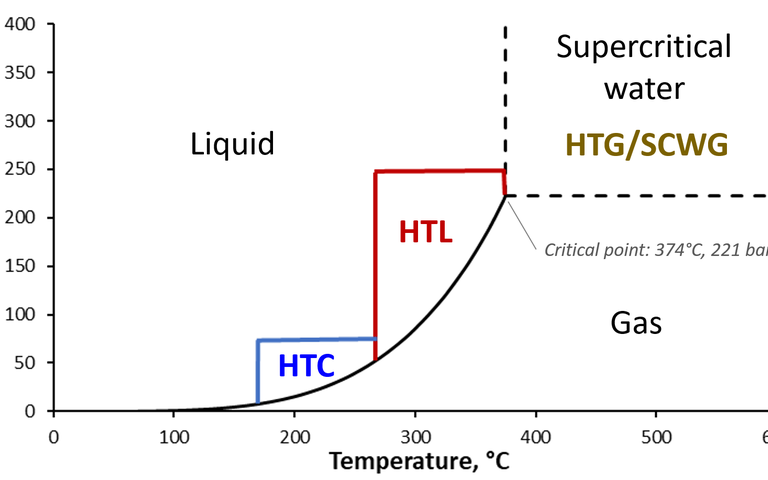
Hydrothermal carbonisation converts sludge predominantly into a hydrochar solid product at temperatures of 180-300 °C
Hydrothermal liquefaction of sewage sludge takes place at temperatures of 250–400 °C and pressures above 40 bar
Hydrothermal gasification converts sludge to a hydrogen and/or methane-rich gas stream at temperatures up to ~550 °C
Oxidative methods for sludge thermal treatment comprise incineration, wet air oxidation and supercritical water oxidation
Non-oxidative thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge refers to treatment at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen
Thickening, dewatering and drying extract water from sludge to reduce the sludge volume
Sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
Sludge is the main waste stream from the treatment of wastewater