
Incineration of sludge
Incineration is the most well established and widely implemented of the sludge thermochemical treatment processes
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.

Oxidative methods for sludge thermochemical treatment comprise incineration, wet air oxidation (WAO) and supercritical water oxidation (SCWO).
These processes convert the combustible organic matter to primarily carbon dioxide and water, along with other gaseous oxidised byproducts (such as nitrogen oxides or NOx) present at lower concentrations, and a solid residue. The methods differ in terms of the operational temperature and pressure, the required feed sludge water content, and the nature and concentrations of gaseous and solid products generated.

Incineration is the most well established and widely implemented of the sludge thermochemical treatment processes
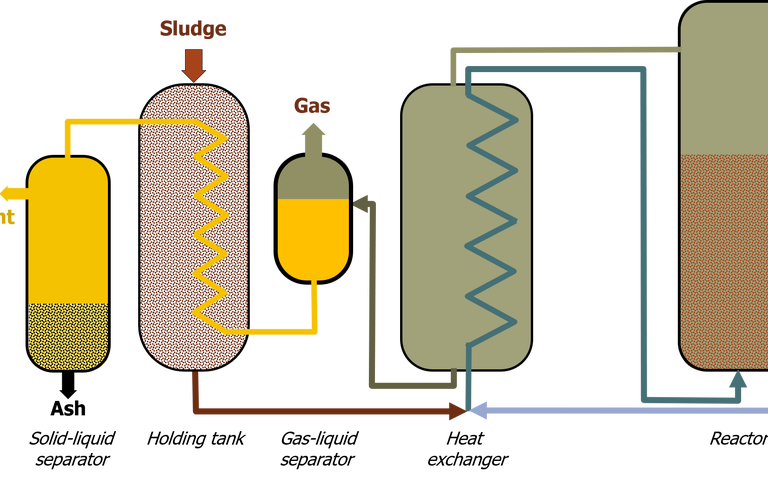
Wet/wet air oxidation of sludge is the thermal degradation, hydrolysis and oxidation of organics at high temperatures

Watermaths: Process Fundamentals for the Design and Operation of Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies − available as an ebook
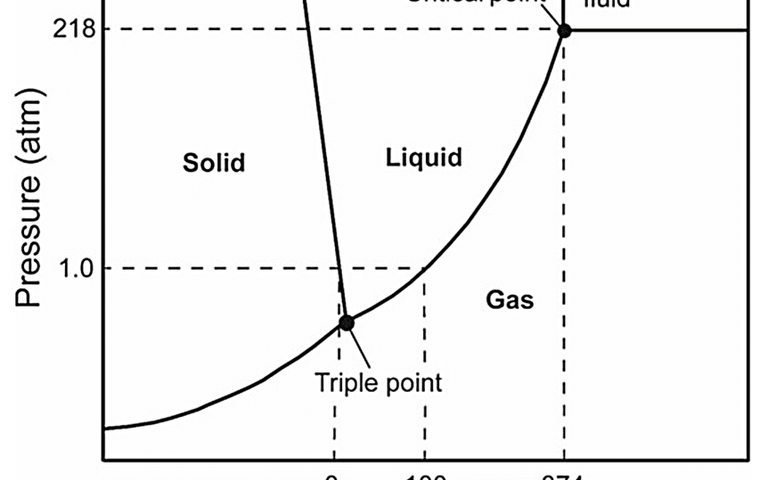
Supercritical water oxidation refers to the oxidation of organics in water in the so-called supercritical phase of water
An example of a Kuzu Grup fluidized bed sludge incineration and energy production plant
Watch video