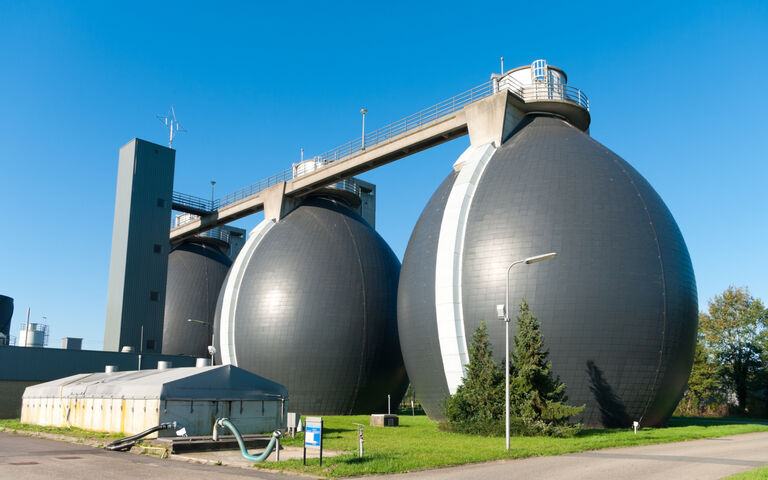

Sludge treatment - the anaerobic digestion process
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is the most extensively employed sludge stabilisation process, and generates a methane gas product
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is the most extensively employed sludge stabilisation process and, as with most sludge and wastewater unit processes, the design and performance of AD depends on the feed characteristics. Professor Simon Judd explains

Anaerobic digestion (AD) is the most extensively employed sludge stabilisation process, and generates a methane gas product
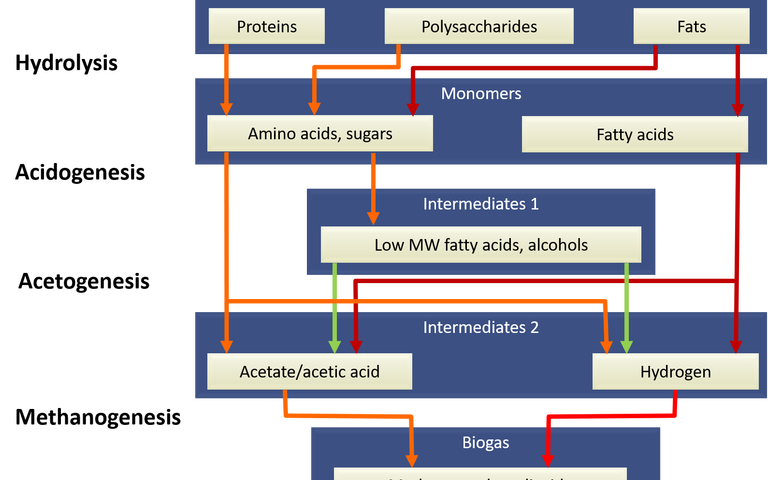
Anaerobic digestion is a multi-step biochemical process comprising hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis

Watermaths: Process Fundamentals for the Design and Operation of Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies − available as an ebook
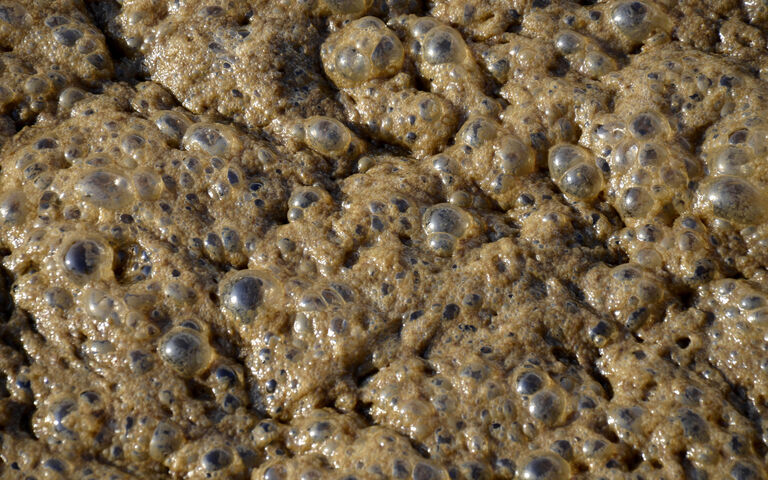

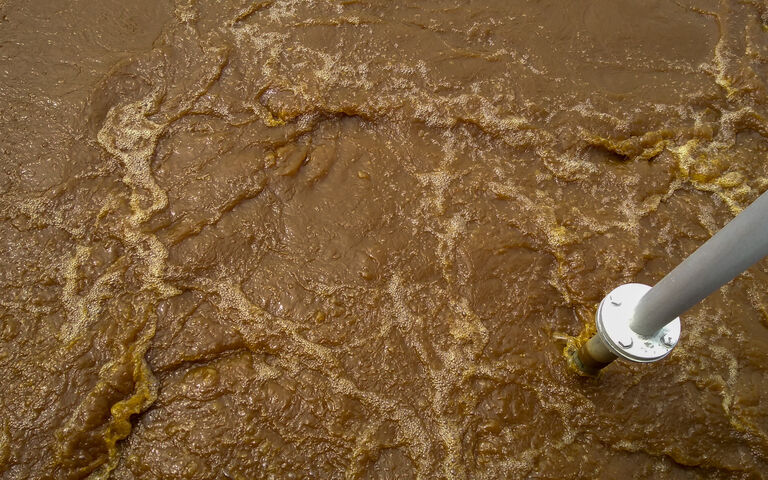
Two widely recognised operational challenges to anaerobic digestion operation are foaming and over-acidification
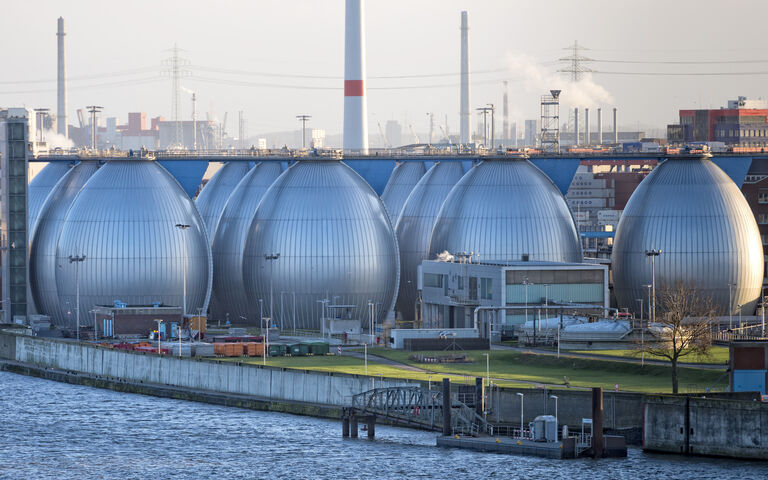

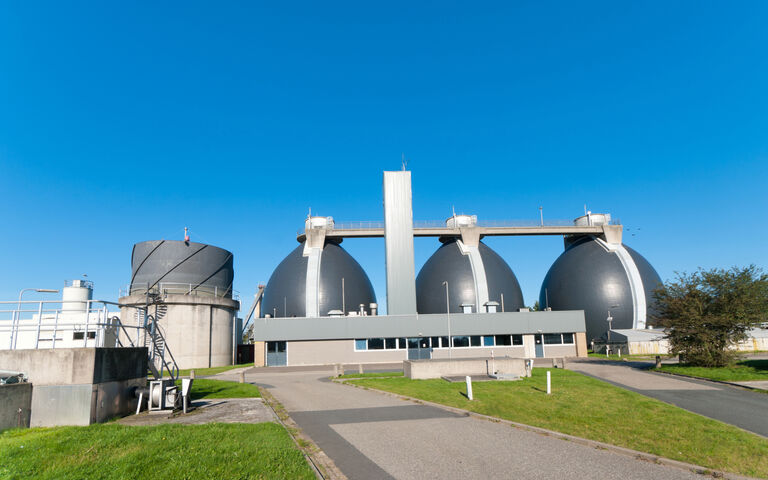
Anaerobic digestion can be a single or multiple tank process, and employ different conditions of stirring and temperature

Learn more

Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more