
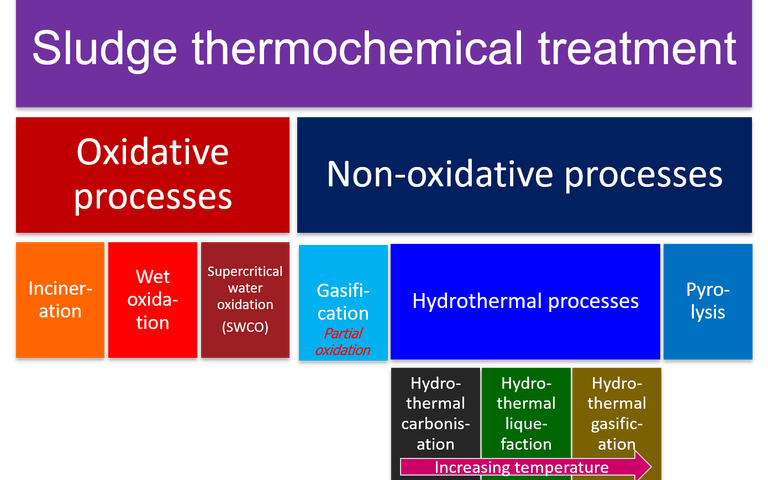
Sludge thermochemical treatment
An introduction to sludge thermochemical treatment methods
Your web browser is out of date.
Update your browser for better security, speed and to get the best experience on this website.
Incineration − or combustion − of sewage sludge is the most widely-implemented alternative end disposal method after land spreading. It oxidatively converts the organic carbon, nitrogen, sulphur, nitrogen and phosphorus into gaseous and predominantly mineral solid products. It is effective in eliminating the feed organics, produces little odour, and generates a stable solid ash product which is stable and reusable. The heat generated can be recovered from the flue gas stream and reused directly and/or converted to electrical power.

An introduction to sludge thermochemical treatment methods
Thermochemical methods are used for either degrading the sludge solids or pre-treating sludge upstream of anaerobic digestion
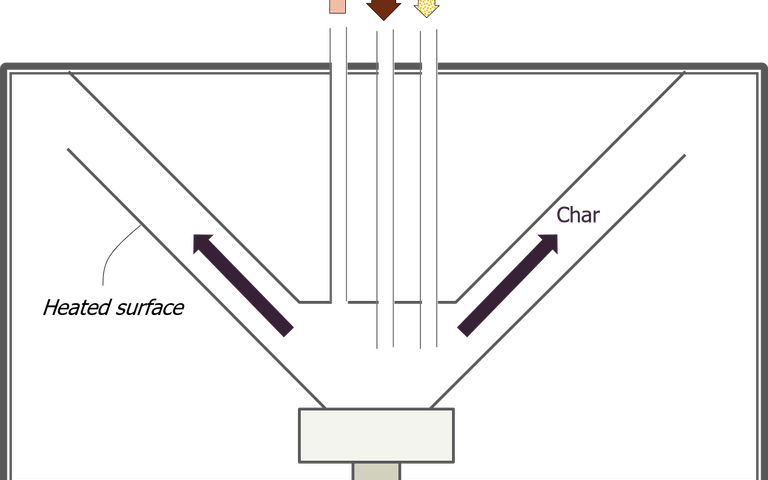
Various reactor configurations exist for sludge thermochemical treatment which vary in design, operation and application

An introduction to oxidative sludge thermochemical treatment methods

Incineration is the most well established and widely implemented of the sludge thermochemical treatment processes
Animation demonstrating the operation of the sewage sludge incineration process − the Buski fluidised bed sludge incineration and energy production plant.
Supercritical water oxidation (SCWO) refers to the rapid oxidation of organics in water in the supercritical phase of water
Wet air oxidation of sludge is the degradation, hydrolysis and oxidation of organic matter at high temperatures and pressures
Oxidative methods for sludge thermal treatment comprise incineration, wet air oxidation and supercritical water oxidation
Non-oxidative thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge refers to treatment at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen
Thickening, dewatering and drying extract water from sludge to reduce the sludge volume
Sludge stabilisation − alkaline stabilisation, lime and solids dosing, plus anaerobic and aerobic digestion
Sludge is the main waste stream from the treatment of wastewater